DRAG DROP (Drag and Drop is not supported)
On an STP network, the root bridge, root port, and designated port are elected in sequence. The election rules of these ports are different. List the steps for electing the root port in sequence.
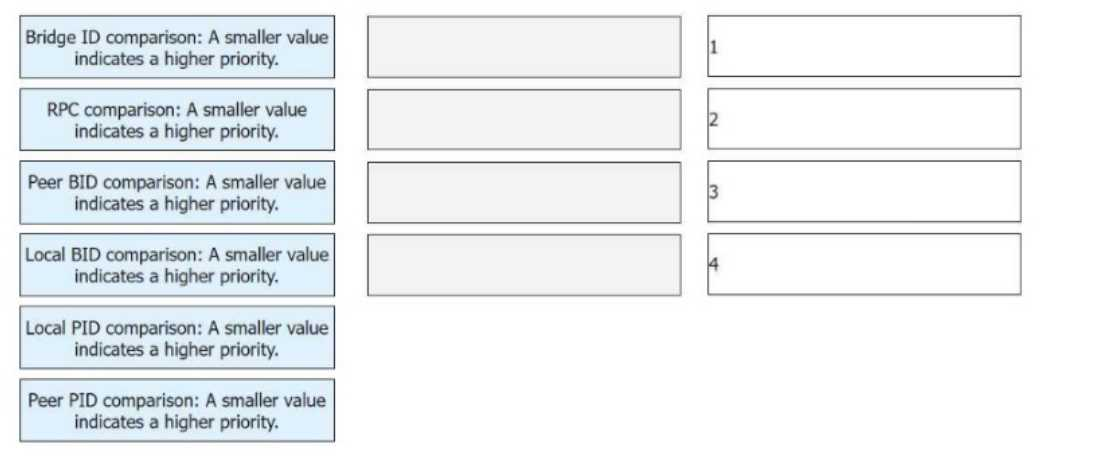
- Refer to Explanation for the Answer
Answer(s): A
Explanation:
The sequence of steps for electing the root port in an STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) network is as follows:
Bridge ID Comparison: The Bridge ID (BID) is compared between the bridges in the network. A smaller value indicates a higher priority, meaning the bridge with the lowest Bridge ID is elected as the root bridge.
RPC (Root Path Cost) Comparison: The path cost to reach the root bridge is calculated. The router with the lowest Root Path Cost (RPC) to the root bridge will have a higher priority for the election of the root port.
Peer BID Comparison: If there is a tie in the Root Path Cost, the Peer BID is compared. A smaller Peer BID indicates a higher priority. This step ensures that if two routers have the same RPC, the one with the lower Peer Bridge ID wins.
Local BID Comparison: If there is still a tie, the Local BID is compared. A smaller Local BID indicates a higher priority. This final step ensures that the router with the lowest local identifier is selected.
Bridge ID Comparison:
The first step in electing the root port is comparing the Bridge IDs. The bridge with the lowest Bridge ID becomes the root bridge. The Bridge ID is made up of the bridge priority and MAC address. The root bridge is the center of the network for STP, and all other ports will calculate their paths based on this root.
Reference:
HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (STP Concepts and Election Process).
RPC (Root Path Cost) Comparison:
Once the root bridge is selected, the network needs to determine the best path to the root. Each port on a non-root bridge will calculate the Root Path Cost (RPC), which is the cumulative cost of reaching the root bridge from that port. The root port is the one that has the lowest RPC, meaning it provides the best path to the root bridge.
HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (STP Path Selection).
Peer BID Comparison:
If multiple paths have the same Root Path Cost, the next step is to compare the Peer Bridge IDs. The bridge with the lowest Peer BID is chosen as the root port. This ensures a tie-breaking mechanism based on the neighbor's identifier.
HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (STP Election Process).
Local BID Comparison:
If there is still a tie after comparing the Peer Bridge IDs, the Local Bridge ID is compared. A smaller Local BID indicates a higher priority, and the port with the lower Local BID will be selected as the root port.
HCIP-Datacom-Core Technology Training Material (STP Local Port Selection).