DRAG DROP (Drag and Drop is not supported)
You are the lead Microsoft Power Platform developer for a company.
Your team of developers are unable to work on the same components at the same time.
The developers have the following requirements:
-A mechanism to automatically push individual changes they make into the existing environments for testing.
-A dedicated environment for all development work.
-The ability to run, but not create, deployments from directly within Microsoft Power Platform.
You need to implement a process to manage the development activities.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
- See Explanation section for answer.
Answer(s): A
Explanation:
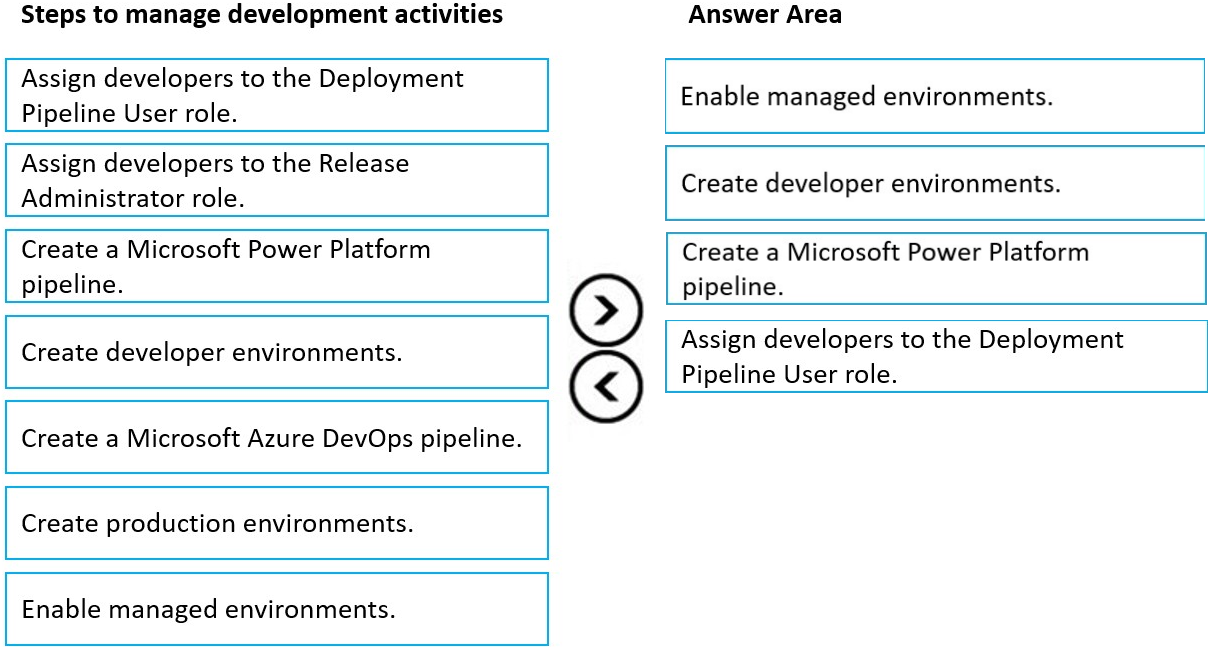
Step 1: Enable managed environments
Set up pipelines in Power Platform
Create or choose environments for pipelines
Before you begin, you need to identify which environments participate in pipelines. Be sure to enable all target environments as Managed Environments.
Note: Managed Environments is a suite of premium capabilities that allows admins to manage Power Platform at scale with more control, less effort, and more insights. Admins can use Managed Environments with any type of environment. Certain features can be configured upon enabling a Managed Environment. Once an environment is managed, it unlocks more features across the Power Platform.
Step 2: Create developer environments
Development environment. This environment is where you develop solutions. A pipeline can be run from within any development environments linked to it.
Incorrect:
* Create production environments
Step 3: Create a Microsoft Power Platform pipeline
Note: Install the pipelines application in your host environment
This step is only required for the initial host setup. You might skip to the next section if you already have access to a host environment where you'll create pipelines.
1. Sign in to the Power Platform admin center, go to Environments > New, and create a new environment with a Dataverse database. Be sure to choose the same region that your development, QA, and production environments are created in.
2. Install the Power Platform Pipelines application in your host environment by selecting the host environment, then select Resources > Dynamics 365 apps.
3. Select Install app and scroll down within the right-side panel until you find Power Platform Pipelines.
4. Select Next, if you agree, accept the terms, and then select Install.
Configure a deployment pipeline [details omitted]
Incorrect:
* Create a Microsoft Azure DevOps pipeline
Step 4: Assign developers to the Deployment Pipeline User role
The Deployment Pipeline User security role grants access to run one or more pipelines. It doesn't grant access to create, edit, or delete pipelines. Users with the Deployment Pipeline User security role won't see the host environment within the environment picker in Power Apps or Power Automate, or otherwise need to be aware of it.
Incorrect:
* Assign developers to the Release Administrator role
Too much permissions.
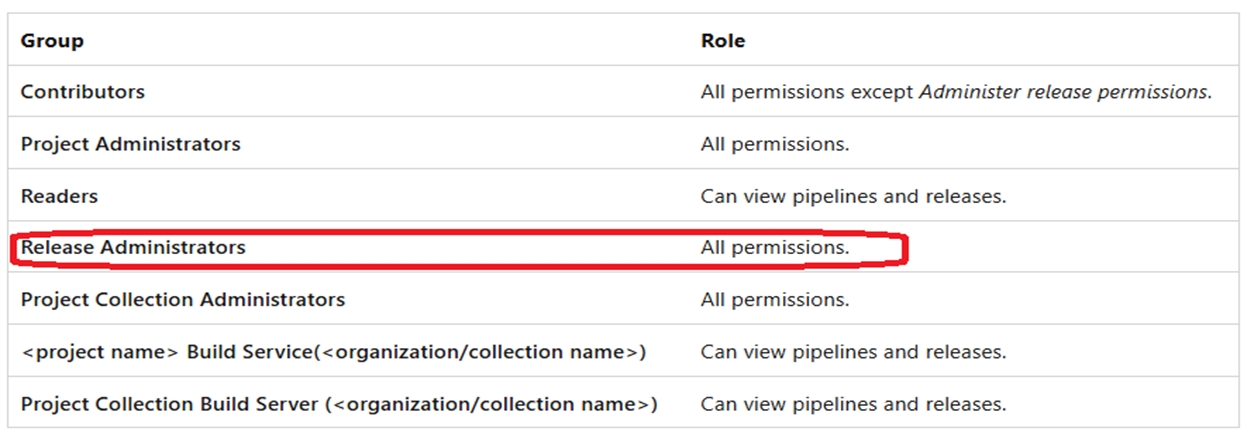
Set release pipeline permissions in Azure Pipelines
Once you create a release pipeline, you can set project-level permissions for all release pipelines and object-level permissions for individual release pipelines and stages. You can also set permissions for release stages, which are a subset of permissions inherited from the object-level release pipeline permissions.
The following table shows the permission hierarchy for release pipelines:
Project-level release pipelines permissions
Object-level release pipeline permissions
Object-level stage permissions
The following table shows default user and group roles:
Reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/alm/set-up-pipelines